Table of Contents
What Is Rest Controller In Spring Boot?
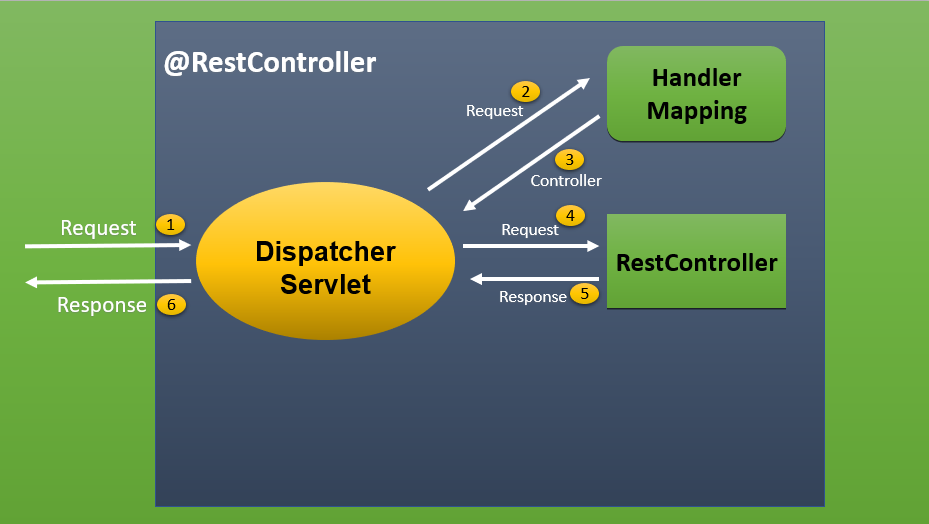
In Spring Boot, a REST Controller is a special type of controller that handles HTTP requests and produces RESTful responses. It’s commonly used to build RESTful APIs in web applications.
To create a REST Controller in Spring Boot, you typically annotate a class with @RestController annotation. This annotation combines @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations, which means that each method in the controller class returns data directly to the client as JSON or XML representation (based on the Accept header of the request).
Here’s an example of a simple REST Controller in Spring Boot:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ExampleController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
@GetMapping("/greet/{name}")
public String greetUser(@PathVariable String name) {
return "Hello, " + name + "!";
}
@PostMapping("/echo")
public String echoMessage(@RequestBody String message) {
return "You said: " + message;
}
}
Let’s break down this example:
@RestControllerannotation marks this class as a REST controller, meaning it will handle incoming HTTP requests and produce HTTP responses.@RequestMapping("/api")annotation specifies the base URL path for all the endpoints defined in this controller. So, all the endpoints in this controller will start with/api.@GetMapping("/hello")annotation defines a handler method for HTTP GET requests to/api/hello. It simply returns “Hello, World!” as the response.@GetMapping("/greet/{name}")annotation defines a handler method for HTTP GET requests to/api/greet/{name}, where{name}is a path variable. It takes the value ofnamefrom the URL path and returns a greeting message.@PostMapping("/echo")annotation defines a handler method for HTTP POST requests to/api/echo. It expects a request body containing a message, which it then echoes back in the response.
In this way, you can define various endpoints in a REST Controller to handle different types of requests and produce appropriate responses.
Difference between @Controller and @Restcontroller in Spring Boot
In Spring Boot, @Controller and @RestController are both annotations used to define classes as controllers, but they serve slightly different purposes:
@Controller:@Controlleris a general-purpose annotation used to mark a class as a controller component in a Spring MVC application.- It is typically used to handle web requests and return a view as a response.
- When a method in a class annotated with
@Controllerreturns a string, it typically represents the name of the view to render. - It’s commonly used in applications where both HTML views and JSON/XML responses are served.
@RestController:@RestControlleris a specialized version of@Controllerintroduced in Spring 4.0 that is tailored for building RESTful web services.- It combines the behavior of
@Controllerand@ResponseBodyannotations, meaning it automatically serializes the return value of methods to JSON or XML and directly returns it as an HTTP response body. - It’s primarily used to build RESTful APIs where the data returned by the controller methods is usually in JSON or XML format, rather than HTML views.
- When a method in a class annotated with
@RestControllerreturns an object, Spring automatically converts it to JSON or XML (based on theAcceptheader) and sends it as the response body.
In summary, while @Controller is more generic and suitable for handling traditional web requests and returning views, @RestController is specifically designed for building RESTful APIs, where the focus is on returning data in JSON or XML format directly to the client.
